If ovarian cysts are a challenge to you, here is everything you need to know about them including the causes, types, symptoms and the natural remedy to cure them.
Women have two ovaries that produce eggs as well as the hormones oestrogen and progesterone which are an important part of the female reproductive system and fertility in general.
An ovarian cyst forms when fluid accumulates in a membrane of an ovary. They often occur during reproductive years.
Ovarian cysts usually disappear on their own but can cause complications if they don’t. Many cysts go away on their own. If not, treatments to get rid of them are going to be required.
Most ovarian cysts are usually small and don’t cause symptoms. In some cases, pressure, bloating, swelling, or pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst, menstrual irregularities, pain during intercourse or irregular bowel movements can occur. This pain may be sharp or dull and may come and go.
A ruptured cyst can cause more sudden severe symptoms and pain. These can include severe pain in the lower belly and bleeding. Fluids or blood may need to be replaced due to internal bleeding. In rare cases, a ruptured ovarian cyst may require surgery.
The ruptured tissues can increase risk for infection if left untreated. Even if the cyst doesn’t rupture, it can sometimes cause the ovary to twist and cut off the blood supply. This is a serious condition called ovarian torsion in which the decreased circulation can cause ovarian tissues to die.
An ovarian cyst may need to be removed if it is suspected of being Cancerous (the chances are more likely in older women), Large (more than 2.5 inches in diameter) and Solid (rather than containing just fluid).
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
The most common causes of ovarian cysts include:
Hormonal problems: Functional cysts usually go away on their own without treatment. They may be caused by hormonal problems or by drugs used to help you ovulate.
Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis can develop a type of ovarian cyst called an endometrioma. The endometriosis tissue may attach to the ovary and form a growth. These cysts can be painful during sex and during your period.
Pregnancy: An ovarian cyst normally develops in early pregnancy to help support the pregnancy until the placenta forms. Sometimes, the cyst stays on the ovary until later in the pregnancy and may need to be removed.
Severe pelvic infections: Infections can spread to the ovaries and Fallopian tubes and cause cysts to form.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Functional cysts are the most common types of ovarian cysts and they include follicle cysts and corpus luteum cysts;
Follicle cysts: During a woman’s menstrual cycle, an egg grows in a sac called a follicle. This sac is located inside the ovaries. In most cases, this follicle or sac breaks open and releases an egg. But if the follicle doesn’t break open, the fluid inside the follicle can form a cyst on the ovary.
Corpus luteum cysts: Follicle sacs typically dissolve after releasing an egg. But if the sac doesn’t dissolve and the opening of the follicle seals, additional fluid can develop inside the sac, and this accumulation of fluid causes a corpus luteum cyst.
Other types of ovarian cysts include:
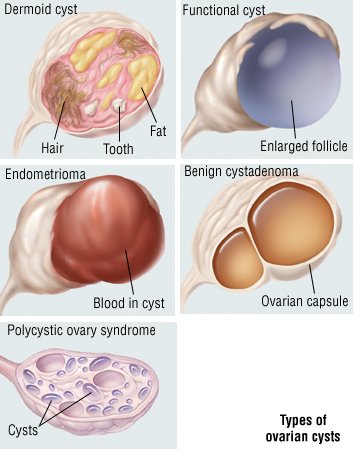
Dermoid cysts: Sac-like growths on the ovaries that can contain hair, fat, and other tissue.
Cystadenomas: Noncancerous growths that can develop on the outer surface of the ovaries
Endometriomas: Tissues that normally grow inside the uterus can develop outside the uterus and attach to the ovaries, resulting in a cyst.
Some ovarian cysts are associated with decreased fertility while others are not. Endometriomas and cysts from polycystic ovarian syndrome may decrease a woman’s ability to get pregnant. However, functional cysts, dermoid cysts, and cystadenomas are not associated with difficulty in getting pregnant unless they are large.
If an ovarian cyst is discovered while you are pregnant, the treatment may depend on the type or size of the cyst.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian cyst symptoms may include:
Ovarian cyst symptoms may include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Painful bowel movements
- Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
- Painful intercourse
- Pain in the lower back or thighs
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
Severe symptoms of an ovarian cyst (ruptured cyst or an ovarian torsion) that may require immediate medical attention include:
- Severe or sharp pelvic pain
- Fever
- Faintness or dizziness
- Rapid breathing
Some women develop a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome. This condition means the ovaries contain a large number of small cysts. It can cause the ovaries to enlarge. If left untreated, polycystic ovaries can cause infertility.
Diagnosing and Treating Ovarian Cyst

Ovarian cyst can be detected during a routine pelvic examination. An ultrasound test (ultrasonography) can also be used. Ultrasonography is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of your internal organs. Ultrasound tests help determine the size, location, shape, and composition (solid or fluid filled) of a cyst.
Imaging tools used to diagnose ovarian cysts include:
CT scan: a body imaging device used to create cross-sectional images of internal organs.
MRI: a test that uses magnetic fields to produce in-depth images of internal organs.
Ultrasound device: an imaging device used to visualize the ovary.
Treatment may be needed to shrink or remove the cyst if it doesn’t go away on its own or if it grows larger. Treatment options include the use of the Ovarian Cyst Remedy Kit which works to shrink and eliminate all sizes and types of ovarian cyst naturally without surgery and no side effects.
Do not forget to share this with other women that you know will benefit from it.
Use the comment box below to ask us any question concerning your health or any of our natural health remedies.
Stay healthy and never give up!
Plan B Wellness
Tel/SMS/WhatsApp: +2348099666650
Email: consult@planbwellness.com
Twitter/Instagram: @planbwellness