Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a serious health condition that can significantly impact a woman’s reproductive health. This extensive write-up aims to provide a thorough understanding of PID, including its causes, symptoms, complications, and the best PID treatment options.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Hidden Threat of PID
- What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
- Causes of PID
- Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of PID
- Complications of Untreated PID
- PID Diagnosis and Treatment Options
- Prevention Tips for PID
- Living with PID: Coping Strategies
- Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Introduction: The Hidden Threat of PID
Imagine living with constant pelvic pain, discomfort during intercourse, and irregular menstrual cycles. For many women, this is their reality due to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID).
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 1 in 8 women with a history of PID experience difficulties getting pregnant.
Therefore, understanding and addressing PID is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an inflammation of the female reproductive organs. It is a serious infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. PID typically occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to these organs.
As a a matter of fact, PID can lead to severe health complications, if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Causes of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Understanding the causes of PID is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
Here are the primary causes of PID:
1. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
The most common and significant causes of PID are sexually transmitted infections. The primary bacteria responsible for PID include:
- Chlamydia trachomatis: This is the most common cause of PID. Chlamydia infections often go unnoticed because they can be asymptomatic or have mild symptoms.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Gonorrhoea is another major cause of PID. Like chlamydia, it can infect the reproductive tract and spread upwards.
When these bacteria infect the lower genital tract, they can ascend to the upper genital tract if left untreated, thereby leading to PID.
2. Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an imbalance in the normal bacterial flora of the vagina. While not directly a sexually transmitted infection, Bacterial vaginosis can increase the risk of developing PID. BV can facilitate the movement of bacteria from the vagina into the reproductive organs, thereby increasing the likelihood of infection.
3. Disruptionof Normal Vaginal Flora
The vagina normally has a balance of different bacteria, primarily lactobacilli, which help maintain a healthy vagina environment. When this balance is disrupted, harmful bacteria can grow more easily and then lead to PID.
Factors that can disrupt normal vaginal flora include:
- Douching: Vaginal douching involves the rinsing or cleaning of the vaginal area with various substances. This practice can alter the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, making it easier for harmful bacteria to ascend into the reproductive organs and lead to PID.
- Frequent Antibiotic Use: Overuse of antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria, allowing harmful bacteria to flourish and cause PID.
4. Post-Surgical and Post-Procedure Infections
Certain medical procedures can increase the risk of PID by introducing bacteria into the reproductive tract.
These procedures include:
- Childbirth: During and after delivery, the risk of infection is heightened.
- Abortion: Both medical and surgical abortions can introduce bacteria into the reproductive tract.
- Insertion of Intrauterine Device (IUD): While IUDs are generally safe, the insertion process can introduce bacteria if not performed under sterile conditions.
5. Poor Sexual Health Practices
Practices that increase the risk of contracting STIs and other infections include:
- Unprotected Sex: Not using condoms or other protective barriers can increase the risk of STIs.
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple sexual partners increases the likelihood of exposure to STIs and by extension, PID.
- Partner with an STI: Having a sexual partner with an untreated STI increases the risk of developing PID.
6. Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system, whether due to chronic illness, certain medications, or lifestyle factors, can make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including those that can lead to PID.
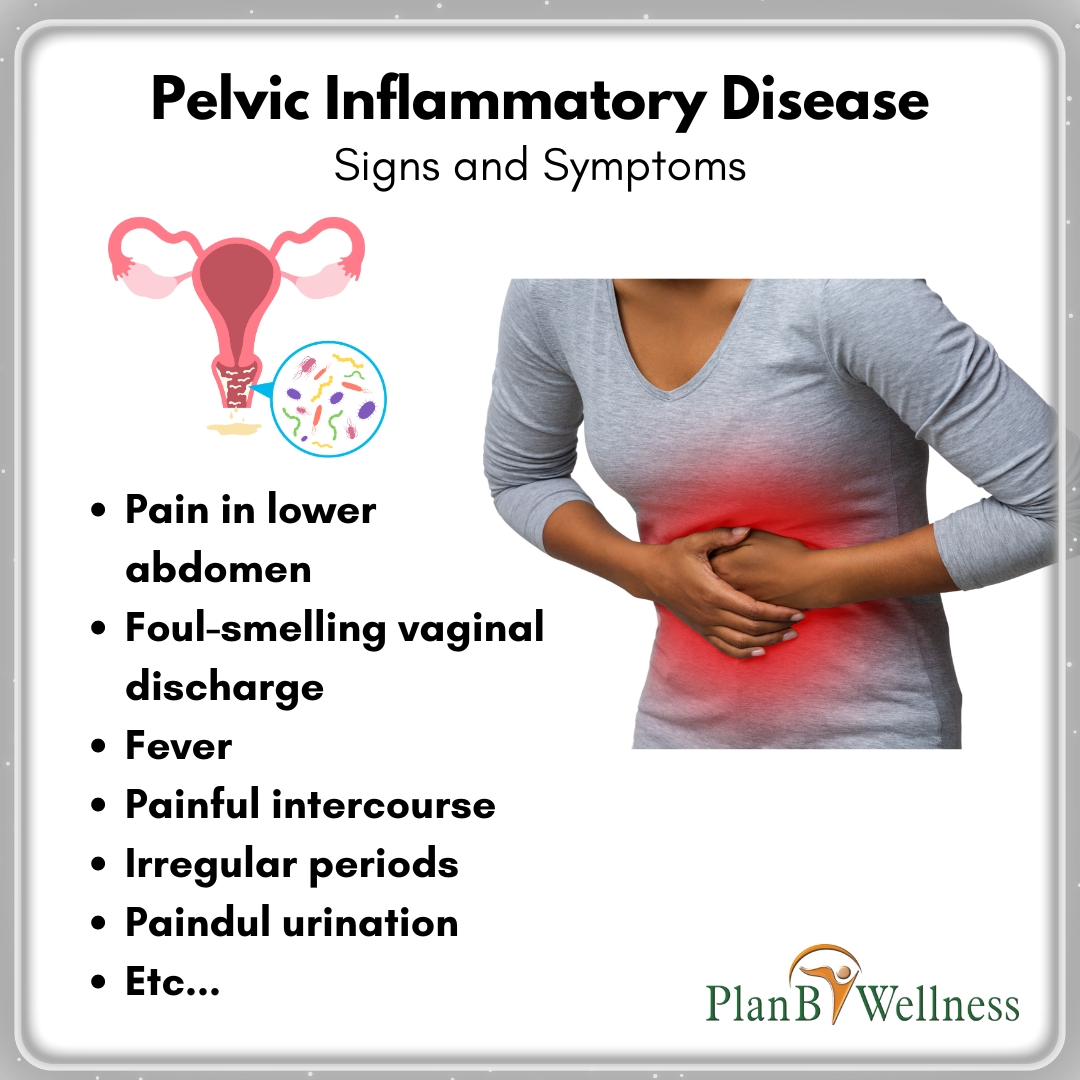
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of PID
PID can be tricky to diagnose because its symptoms often mimic those of other conditions. However, recognizing the signs and symptoms of PID is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Here, we explore the various symptoms associated with PID and how they manifest.
Common Symptoms of PID;
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or recurrent pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis. This is the most common symptom of PID. The pain can range from mild to severe and it’s often described as a dull ache or sharp, stabbing sensation.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdominal region. Similar to pelvic pain, this discomfort can vary in intensity and may be constant or intermittent.
- Unusual Vaginal Discharge: Abnormal vaginal discharge that may be yellow, green, or have an unusual odour. This symptom is a result of the infection causing inflammation and discharge from the reproductive organs.
- Pain During Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia). Painful intercourse can be a sign of inflammation and infection in the reproductive organs.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or pain when urinating (dysuria). This symptom may be mistaken for a urinary tract infection (UTI) but can also be a sign of PID.
- Irregular Menstrual Bleeding: Bleeding between periods or after sexual intercourse. Irregular bleeding can be a sign of infection and inflammation affecting the endometrium and other female reproductive tissues.
- Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Periods: Menstrual periods that are heavier or last longer than usual. This can occur due to the infection causing changes in the endometrial lining.
- Fever and Chills: Elevated body temperature and chills. Fever is a common sign of infection and can indicate that the body is fighting off the bacteria causing PID.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. Chronic infections like PID can cause ongoing fatigue due to the body’s continuous efforts to fight the infection.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting. These symptoms are less common but can occur in severe cases of PID.
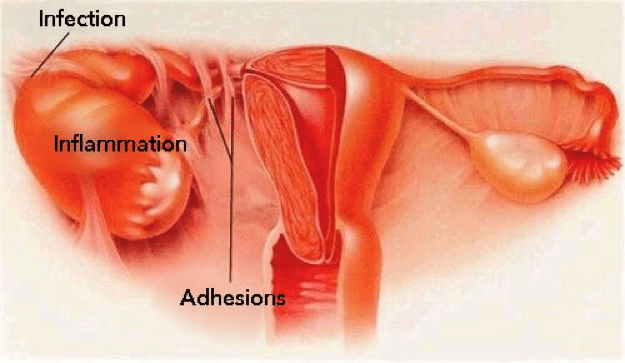
Complications of Untreated Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease can lead to severe and lasting health complications if left untreated. Understanding these potential complications emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment of PID.
Below, we delve into the various complications associated with untreated PID and how they can impact a woman’s health.
1. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis. This pain can linger for months or even years after the initial infection has been treated. The pain is often a result of the scarring and inflammation caused by PID. This ongoing discomfort can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life, making everyday activities challenging.
2. Infertility: One of the most severe complications of untreated PID is infertility. The infection can cause scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes, which can prevent sperm from reaching an egg or impede the fertilized egg’s journey to the uterus. As mentioned earlier, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 1 in 8 women with a history of PID experience difficulties getting pregnant.
3. Ectopic Pregnancy: Scarring from PID can cause a fertilized egg to implant and grow in the fallopian tube rather than the uterus. This is known as an ectopic pregnancy, which is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. Ectopic pregnancies cannot proceed normally and can cause the fallopian tube to burst, leading to severe internal bleeding.
4. Tubo-Ovarian Abscess: In severe cases, PID can lead to the formation of abscesses in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. These abscesses can be life-threatening if they rupture or cause widespread infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to drain the abscess.
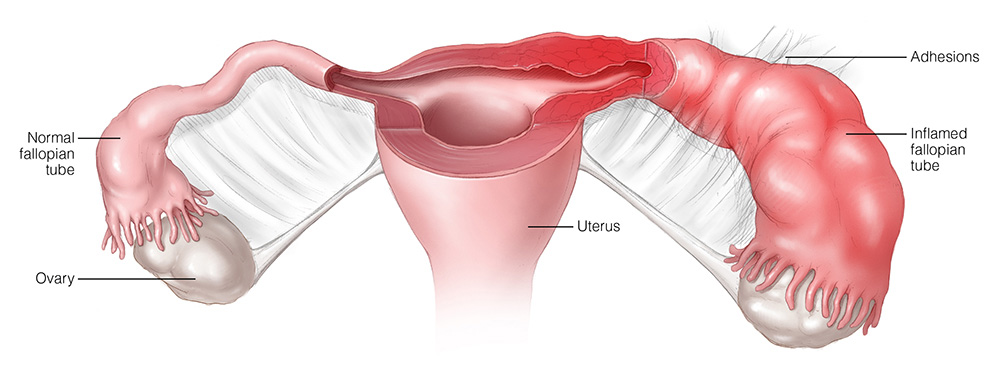
5. Adhesions and Scarring: PID can cause adhesions, which are bands of scar tissue that can form between the pelvic organs. These adhesions can lead to chronic pain, bowel obstruction, and difficulties with future pregnancies. The scarring can also make surgical procedures more complicated. Click here to read more about adhesions/scar tissues and the natural remedy to overcome them.
6. Increased Risk of STIs: Women with PID are at a higher risk of contracting other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) because the inflammation and damage to the reproductive tract make it easier for pathogens (germs) to invade.
7. Persistent Infection: Some women may experience recurrent or persistent infections even after receiving treatment for PID. This can occur if the initial treatment was not completely effective or if the individual is re-exposed to the infection.
8. Recurrent PID: Women who have had PID once are at higher risk of getting it again. Each subsequent infection increases the likelihood of severe complications, including infertility and chronic pelvic pain.
How is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Diagnosed?
How do you know if your have PID?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) can be challenging to diagnose due to its often subtle, hideen and varied symptoms. However, early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and begin appropriate treatment.
Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process for PID:
1. Medical History
- Discussion with the Patient: The healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history. This includes asking about the patient’s symptoms, sexual history, contraceptive use, and any past occurrences of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Symptom Inquiry: Specific questions about pain in the pelvic area, unusual vaginal discharge, painful urination, and any other related symptoms will help the doctor understand the extent and nature of the condition.
2. Physical Examination
- Pelvic Examination: A thorough pelvic exam is essential for diagnosing PID. During the examination, the healthcare provider will check for signs of tenderness in the reproductive organs (uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries) and look for abnormal discharge or signs of infection.
- Cervical Motion Tenderness: The health provider may move the cervix slightly to see if it causes pain, which can indicate PID.
3. Laboratory Tests
- Cervical Cultures: Samples from the cervix and vagina are taken to test for STIs such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea, which are common causes of PID.
- Urine Tests: Urinalysis can help identify infections in the urinary tract that may be associated with PID.
- Blood Tests: These tests can detect markers of infection and inflammation, such as elevated white blood cell counts and C-reactive protein levels.
4. Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: Pelvic ultrasound is often used to get a detailed view of the reproductive organs. It can help identify abnormalities such as abscesses, fluid accumulation, or swollen fallopian tubes.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This type of ultrasound provides a closer look at the internal reproductive organs and can offer more precise images.
5. Endometrial Biopsy
- Tissue Sample: In some cases, a small sample of the endometrial tissue (lining of the uterus) is taken to look for signs of inflammation or infection. This is usually done if other tests are inconclusive.
6. Laparoscopy
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure where a small camera is inserted through a tiny incision in the abdomen to visually inspect the pelvic organs. This method is more invasive but provides a direct view of the reproductive organs and can confirm the presence of PID.
- Direct Observation: This procedure allows for the direct observation of the pelvic organs and the opportunity to obtain tissue samples for further examination.
7. Differential Diagnosis
- Ruling Out Other Conditions: The healthcare provider will also consider other conditions that could cause similar symptoms, such as ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, or ovarian cysts, and use diagnostic tests to rule them out.
Why Most Antibiotics Fail in Curing PID
The amount of enquiries we get daily from women who have used different kinds of antibiotics (in both capsules, tablets and injections) to treat PID but failed are so enormous. The questions they always ask is – why?
Read on to find out why antibiotics may not work effectively for PID.
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat PID, but there are several reasons why they may fail to provide a complete cure. Understanding these reasons is crucial in managing and treating PID effectively.
1. Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment
- Asymptomatic Infections: Many women with PID may not exhibit symptoms until the infection has significantly progressed. This delay can lead to more extensive damage to the reproductive organs, making it harder for antibiotics to fully eradicate the infection.
- Chronic PID: Chronic or recurrent PID, where the infection persists or reoccurs, can be more resistant to antibiotic treatment.
2. Incomplete Treatment Regimens
- Non-Adherence to Medication: Patients may not complete their prescribed course of antibiotics, either due to side effects or feeling better before the medication course is finished. This can result in the infection not being fully eradicated and becoming resistant.
- Incorrect Dosage: Incorrect dosing or inappropriate antibiotic choice can lead to suboptimal treatment outcomes.
3. Polymicrobial Infections
- Mixed Infections: PID is often caused by multiple types of bacteria, including anaerobes, which are harder to treat. Standard antibiotic regimens may not cover all the bacterial strains involved, leading to incomplete or failed treatment.
- Biofilm Formation: Some bacteria can form biofilms, which are protective layers that make them more resistant to antibiotics. This can prevent the antibiotics from reaching and effectively killing the bacteria.
4. Antibiotic Resistance
- Resistant Strains: The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. These resistant strains are harder to treat and may not respond to standard antibiotic therapies.
- Global Health Concern: Antibiotic resistance is a growing global health concern, affecting the efficacy of treatments for various infections, including PID.
5. Underlying Health Conditions
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions may not respond as well to antibiotic treatment. Their bodies are less capable of fighting off the infection, even with antibiotic support.
- Concurrent Infections: Co-infections with other STIs or infections can complicate the PID treatment and make antibiotics less effective.
6. Anatomical Barriers
- Tissue Damage: PID can cause significant damage and scarring to the reproductive organs, creating physical barriers that antibiotics cannot easily penetrate. This can leave pockets of infection that are not reached by the medication.
- Abscess Formation: Abscesses or collections of pus within the pelvis can be difficult to treat with antibiotics alone.
7. Behavioural and Lifestyle Factors
- Reinfection: Continued exposure to sources of infection, such as unprotected sexual contact with an infected partner, can lead to reinfection and ongoing PID issues. Without addressing these behaviours, antibiotics alone may not provide a lasting cure.
- Lack of Partner Treatment: If sexual partners are not treated simultaneously, the risk of reinfection remains high, undermining the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment. This particular one is not for antibiotics only, it’s similar for other forms of treatment for PID as well. If you are sexually active, it is advisable to treat PID or any related infection along with your partner.
Addressing the Limitations of Antibiotics in Treating PID
Given the limitations of antibiotic treatment for PID, it is essential to consider a better and more comprehensive approach to managing the disease.
Introducing PID Remedy – A Natural Solution for PID
Antibiotics are not always the ultimate answer to treating PID due to the various challenges outlined above. For those seeking a natural, safer and more comprehensive alternative, PID Remedy offers a safe and effective solution.
Crafted with a unique blend of organic herbs, PID Remedy targets the root causes of PID, eliminating inflammation and promoting reproductive health.
Why Choose PID Remedy?
- Natural Ingredients: PID Remedy is crafted with a unique blend of herbs known for their anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. These ingredients have been used for centuries in traditional medicine to combat infections and promote healing with no adverse effects. Not only that, the ingredients are backed by verifiable scieitific researches that confirm their effectiveness in combating PID.
- Comprehensive Action: Unlike antibiotics, which may only target certain bacterial strains, PID Remedy works on multiple fronts. It helps to:
- Reduce Inflammation: Alleviates pain and discomfort by soothing inflamed tissues.
- Boost Immunity: Strengthens the body’s natural defenses to fight off infections.
- Promote Healing: Supports the repair of damaged reproductive tissues and prevents scarring.
- Preventing Recurrence: PID Remedy not only addresses the current infection but also helps to prevent future recurrences by maintaining a healthy balance in the reproductive system.
- No Antibiotic Resistance: Being a natural remedy, it doesn’t contribute to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance, making it a safer long-term option.
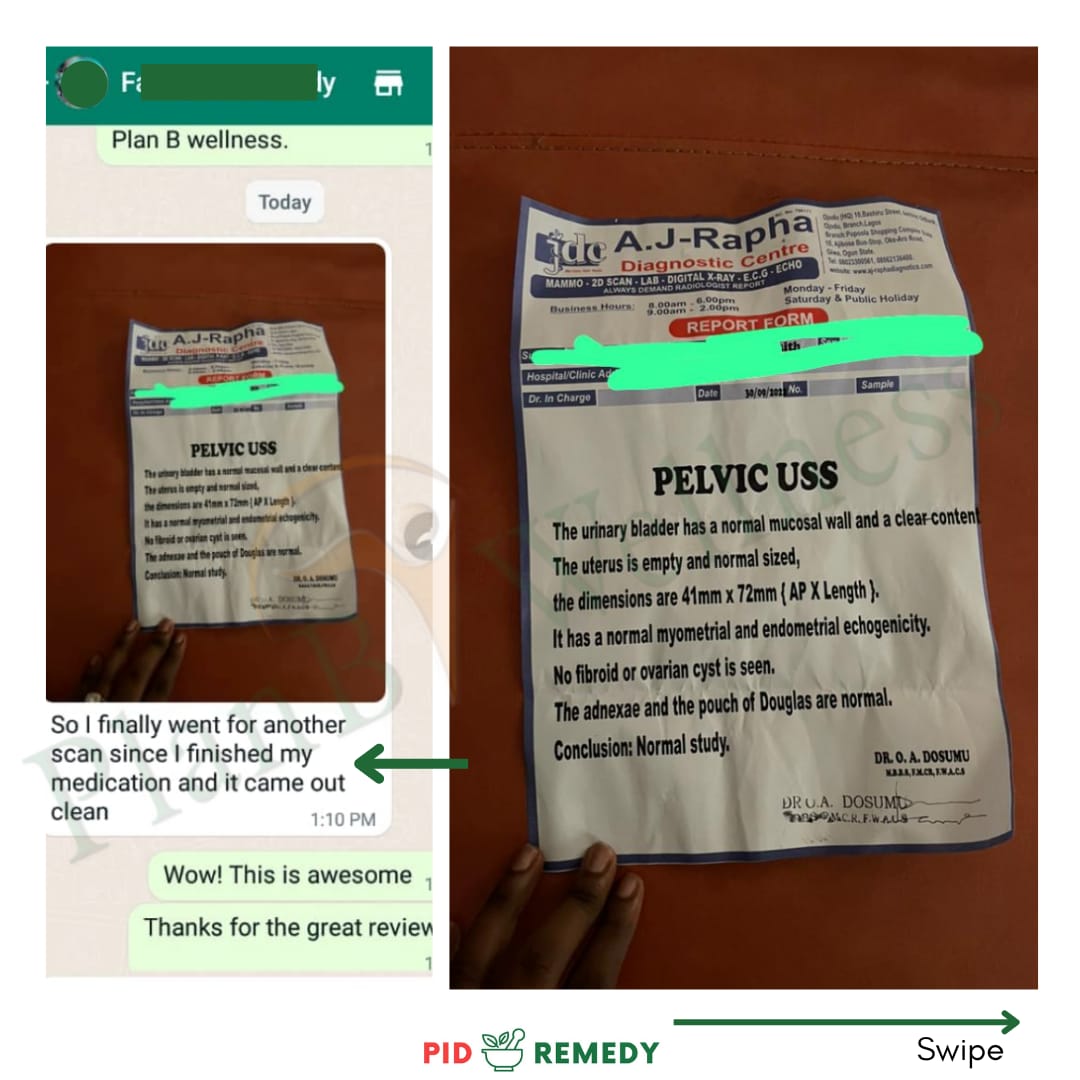
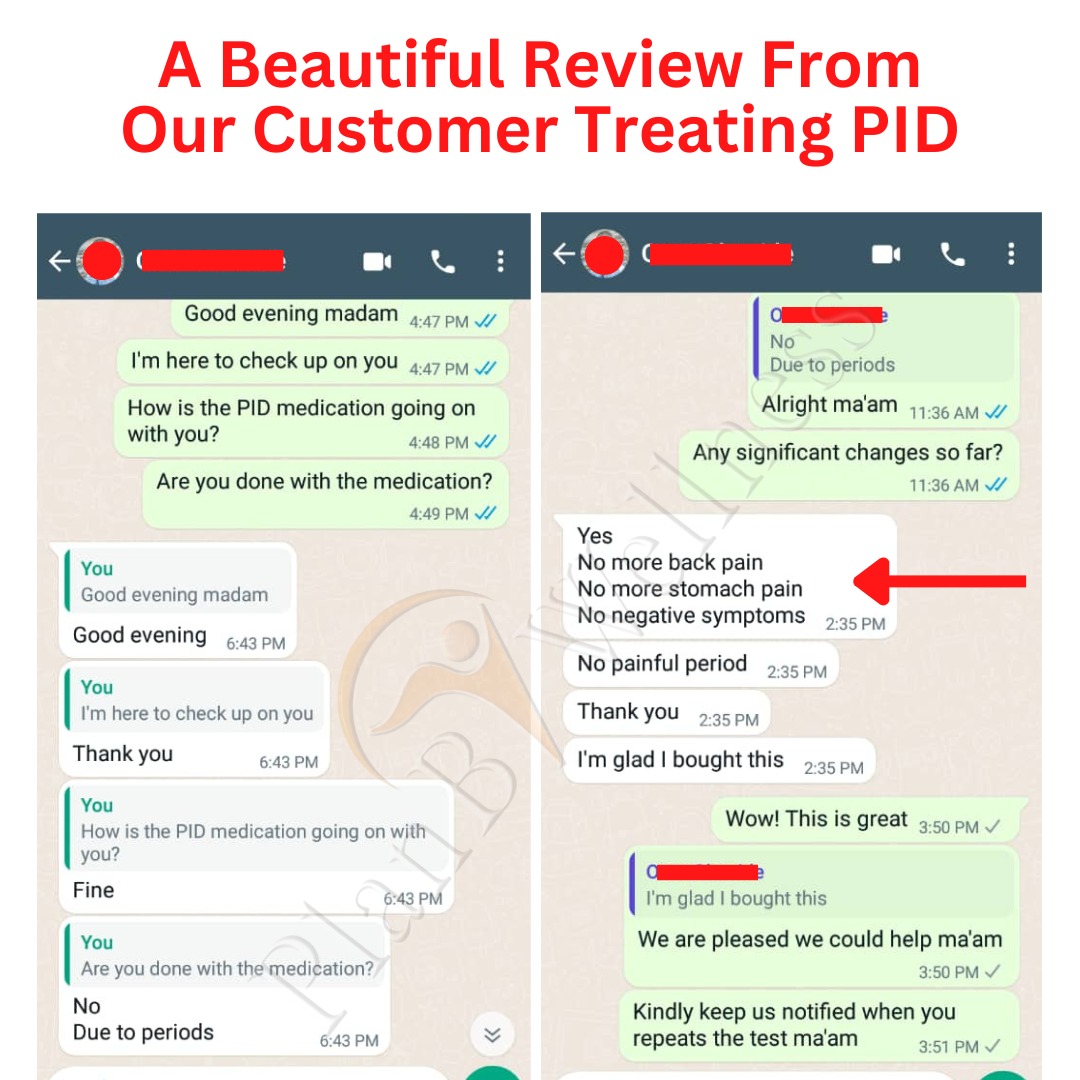
See Testimonials from Satisfied Customers:
PID Prevention Tips
Preventing PID involves maintaining good sexual health and hygiene practices:
- Regular STI Screenings: Early detection and treatment of STIs can prevent PID.
- Safe Sex Practices: Use condoms and limit the number of sexual partners.
- Prompt Treatment: Address any infections promptly to prevent them from spreading.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
Understanding PID is the first step toward taking control of your reproductive health.
If you suspect you have PID, seek medical advice promptly. And remember, early treatment can prevent serious complications.
For a natural and effective treatment for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, try our PID Remedy. The product is designed to address the root causes of PID, providing relief and promoting reproductive health.
See More Customers Testimonial Below;
Order Your PID Remedy Today: Click here to learn more and place your order. Free and fast nation-wide doorstep delivery available.
If you have any question about PID or regarding your fertility or health in general, feel free to drop a message for us in the comment box below and a member of our team will respond to your as fast as possible.
Our contact details can also be found below for further enquiries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About PID
Q: What causes PID?
A: PID is usually caused by sexually transmitted bacteria, such as those from chlamydia and gonorrhoea. It can also result from bacterial vaginosis or post-surgical infections.
Q: What are the common symptoms of PID?
A: Common symptoms include pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, painful urination, irregular menstrual bleeding, and unusual vaginal discharge.
Q: How is PID diagnosed?
A: PID is diagnosed through pelvic examinations, ultrasounds, and sometimes laparoscopy. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
Q: What are the long-term complications of untreated PID?
A: Untreated PID can lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, Fallopian tube blockage, chronic pelvic pain, and the formation of abscesses in the reproductive tract.
Q: How can PID be prevented?
A: Preventing PID involves regular STI screenings, practicing safe sex, and promptly treating any infections to prevent them from spreading.
Q: What is PID Remedy?
A: PID Remedy is a natural herbal solution designed to target the root causes of PID, reduce inflammation, and promote reproductive health.
Q: Are there any testimonials from women who have used PID Remedy?
A: Yes, many women have successfully used PID Remedy to overcome PID. Click here to see what they have to say.
Q: How can I order PID Remedy?
A: You can order PID Remedy by clicking here or by calling or messaging our official lines: 08099666648 or 08099666658.
Q: Can I book a consultation with your company?
A: Yes. We offer both virtual/online and walk-in consultations. For online consultation, kindly call or chat any our official lines on WhatsApp: 08099666648 or 08099666658. For physical consultation, feel free to visit out office (see the address below).
Stay healthy and never give up!
Plan B Wellness
Email: consult@planbwellness.com
Consultation (Whatsapp/Call/Text): +2348099666648, +2348099666658
Instagram: @planbwellnessofficial
Office Address: 53, Anisere bus stop, Governor’s road, Ikotun, Lagos, Nigeria








Thanks for your explanation for pid . you made my day for understanding it.
Thank you for the explanation please can I get remedy for the PID
Kindly reach out to us on whatsapp on 08130566655
Our support team in on standby to serve you.
Regards