It is a medical fact that some health challenges affect women differently and more commonly. Those are the ailments we will be looking at in the write-up.
For example, women experience some unique and specific health-related issues ranging from pregnancy and menopause to gynaecological conditions, such as uterine fibroids, tubal blockage, adhesions, pelvic floor disorders and so on which are peculiar to the female gender only.
Below, we will examine some of these women-specific ailments, how they affect women and what to do to prevent or cure them as the case may be.
BREAST CANCER

Breast cancer, which typically originates in the lining of the milk ducts, can spread to other organs, and it is the most aggressive cancer affecting the global female population.
Initially, women afflicted with breast cancer may develop breast lumps. Most breast lumps are nonthreatening, but it is important for women to have each lumps checked by a care provider.
WHAT ARE BREAST LUMPS?
A breast lump is a localized swelling, protuberance, bulge, or bump in the breast that feels different from the breast tissue around it or the breast tissue in the same area of the other breast.
Possible causes of breast lumps include:
- an abscess or infection
- adenoma or fibroadenoma
- cysts
- fat necrosis
- lipoma
- breast cancer
A lump can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (nonmalignant).
You might develop a lump in your breast but it doesn’t mean you have breast cancer.
Breast cancer is only confirmed when the lump in your breast is malignant or cancerous lumps.

CANCEROUS LUMP
A breast cancer lump or tumor usually feels hard or firm. It typically has an irregular shape, and it may feel as if it is stuck to the skin or deep tissue within the breast.
Breast cancer is not usually painful, especially in the early stages. It can develop in any part of the breast or nipple, but it is most common in the upper outer quadrant.
Some malignant tumors are painful. This can happen when they are large, and if they cause other structures in the breast to be compressed, or if they ulcerate or grow through the skin.
It is important for women to be familiar with their bodies and their breasts. Knowing how the breasts normally feel can help to recognize any problematic changes or lumps.
In Nigeria, about 10,000 cancer deaths are recorded annually while 250,000 new cases are recorded yearly.
It is also worrisome that only 17 percent of African countries are said to have sufficiently funded cancer control programmes, while less than half of all countries in the world have functional plans to prevent the disease and provide treatment and care to patients.
HOW DOES BREAST CANCER DEVELOP?
Changes or mutations in DNA can cause normal breast cells to become cancer. Certain DNA changes are passed on from parents (inherited) and can greatly increase one’s risk for breast cancer.
Other lifestyle-related risk factors, such as what you eat and how much you exercise, can increase your chance of developing breast cancer, but it’s not yet known exactly how some of these risk factors cause normal cells to become cancer.
Hormones seem to play a role in many cases of breast cancer, but just how this happens is not fully understood.
FIVE EARLY SIGNS OF BREAST CANCER THAT CAN BE OVERLOOKED
1. Persistent Cough
Dry cough, shortness of breath, and sore throat may indicate that cancer cells have spread to the lungs.
A problem is known as secondary breast cancer and occurs in 60 to 70 percent of women who become terminally ill. Yet, most patients overlook these symptoms because they mimic those of other less serious conditions, such as common cold and flu.
Cancer cells can irritate the pleura (the lining around the lungs), causing difficulty breathing and fluid build up. Some women may also experience chest pain and hoarse throat that doesn’t subside. If these symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, consult your doctor immediately.
2. A New Mole
Even though moles are usually linked to an increased risk of skin cancer, it’s not always the cause. A study conducted on 5,956 women has found that those with the most moles had a 13 percent higher risk of breast cancer. The risk appears to be higher in pre-menopausal women with many moles.
3. Digestive Problems
Abdominal bloating, constipation, bladder incontinence, and tenderness are among the main signs of breast cancer. This disorder causes hormonal changes that affect digestion and organ function.
Some patients experience loss of bladder control when laughing, coughing, or sneezing. Others report a sudden need to urinate.

Cancer puts stress on your body and messes up your hormones, which can upset the digestive system. Abdominal or pelvic pain, changes in bowel habits, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, and swelling in the abdominal area indicate that something is happening in your body. If you notice any of these symptoms, get some tests done.
4. Back Pain
Eight out of 10 people will experience back pain at some point. Prolonged sitting, poor posture, bad lifting form, arthritis, and injuries can increase your risk of back pain. Unfortunately, this symptom might also indicate that breast cancer cells have spread to your spine.
Cancer-related back pain feels as though it’s coming from the bone, putting pressure on the spine and ribs. Some women have trouble moving around or sleeping at night because of it.
The pain can weaken your bones, leading to fractures. Most times, back pain caused by cancer is accompanied by nausea, confusion, thirst, irritability, tiredness, and constipation. The good news is that treatment can be started long before your bones become weak enough to cause throbbing pain and affect your everyday life.
5. Others
Menstrual changes, heartburn, upset stomach, lymph nodes in the armpit, and difficulty eating are some of the most common yet overlooked signs of breast cancer.
Check your breasts regularly for lumps, hard knots, swelling, and nipple discharge.
In its early stages, breast cancer may also cause headaches, loss of balance, blurred vision, constant nausea, difficulty urinating, and numbness anywhere in your body. If you notice these symptoms that don’t go away within two weeks, seek medical help.
Watch out for these signs and let your doctor know about it. Breast cancer symptoms vary from one individual to another. Don’t wait for a lump to show up in your breasts; by that time, it could be too late to get treatment.
If you have any signs of cancer, stay calm and talk with a professional at Plan B Wellness Limited. Remember that breast cancer can be successfully cured.
Steps for a Breast Self-examination
The following guidelines will help women carry out a self examination of their breast;
- Looking in a mirror, check the size, shape, colour and look for visible swellings or lumps
- Raise the arms and repeat step 1.
- Check for any discharge from the nipples that may be watery, milky, yellow, or with blood.
- Feel the breasts with a firm, smooth motion while lying down, including under the arms and down to the ribcage.
- Repeat step 4 while standing or sitting, it may be easier in the shower.
Even though most breast lumps are benign (noncancerous), anything unusual should be checked by a doctor.
TREATMENT
While it is worth seeing a doctor about any breast lump that causes concern, treatment is not often needed, depending on the cause of the lump.
The doctor will carry out a physical examination and they may recommend a mammogram or ultrasound scan to check what kind of lump is present.
If there is a cyst or a fibrous lump, they may recommend monitoring the lump but not taking any further action.
If there is an abscess, the doctor may lance and drain it with a fine needle, and prescribe antibiotics.
If the doctor suspect cancer, a biopsy may be taken. If cancer is found, treatment usually involves surgery and chemotherapy or radiation therapy, depending on the stage of the cancer.
A test for changes in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes may be recommended. If this gene is present and breast cancer has occurred, preventive surgery may be an option to prevent a recurrence.
Most breast lumps are not cancerous, but it is a good idea to have them checked by a medical professional.
If you desire a natural remedy for breast cancer, click here to check one out.
HOW TO LIMIT YOUR RISK OF BREAST CANCER
- Reduce your alcohol
- Don’t smoke
- Control your weight
- Be physically active
- Limit dose and duration of hormone therapy
- Avoid exposure to radiation and environmental pollution
MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER
If you already have breast cancer, the mainstay of breast cancer management is surgery for the local and regional tumour, followed (or preceded) by a combination of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, endocrine (hormone) therapy, and targeted therapy depending on the stage of the cancer.
Research is ongoing for the use of immunotherapy in breast cancer management.
Meanwhile, the public is now aware of the numerous negative side effects of chemotherapy and the need for a less-risky approach such as this natural and holistic remedy for breast cancer.
2. OVARIAN AND CERVICAL CANCER

Cervical cancer originates in the lower uterus, while ovarian cancer starts in the Fallopian tube. While both conditions cause similar pain, cervical cancer also causes discharge and pain during intercourse.
While ovarian cancer presents extremely vague symptoms, the condition is very complex. Finally, Pap smears detect cervical but not ovarian cancer.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF OVARIAN AND CERVICAL CANCER
- PAIN: In advanced cervical cancer, patients can have pain in the legs, pelvis or back. With ovarian cancer, patients can have pelvic pain, or a sense of pelvic heaviness. Back pain can also occur, which worsens as the disease progresses. Ovarian cancer patients may have abdominal pain and discomfort.
- SWELLING: For example, patients with ovarian cancer may become bloated, which can occur with increased gas. Patients may also have a swollen stomach or abdomen. In advanced cervical cancer, patients can have swelling in one leg.
- CHANGES IN APPETITE AND WEIGHT: Patients with cervical or ovarian cancer may have changes in appetite, which can affect their weight. For example, both cervical and ovarian cancer patients can have a loss of appetite. However, some ovarian cancer patients may gain weight. Ovarian cancer can also cause patients to feel full quickly after eating or they may have problems eating. The appetite and weight changes can occur along with nausea and vomiting
- BOWEL AND BLADDER PROBLEMS: Ovarian and cervical cancer can cause bowel and bladder problems for patients. For example, ovarian cancer patients can experience constipation. Patients may also have increased need to urinate. In advanced cervical cancer, patients can have urine or feaces leak from their vaginas.
- OTHER SYMPTOMS: Patients with cervical cancer can have continuous vaginal discharge, which can appear bloody, pale, brown, watery or pink, and the discharge may smell foul. In advanced cervical cancer, patients can experience fatigue and may have bone fractures. With ovarian cancer, patients may have excessive hair growth.
HOW TO REDUCE YOUR RISK OF OVARIAN AND CERVICAL CANCER
There is no known way to prevent ovarian cancer, but the following are associated with a lower chance of getting ovarian cancer;
- Having used birth control pills for five or more years.
- Having had a tubal ligation (getting your tubes tied), both ovaries removed, or a hysterectomy (an operation in which the uterus, and sometimes the cervix, is removed).
- Having given birth.
- Breastfeeding. Some studies suggest that women who breastfeed for a year or more may have a modestly reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
While these things may help reduce the chance of getting ovarian cancer, they are not recommended for everybody, and risks and benefits are associated with each.
Avoiding risk factors may lower your risk, but it does not mean that you can not get cancer. Talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk.
TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF OVARIAN AND CERVICAL CANCER
Treatment for ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy.
Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation.
Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
Treatment for cervical cancer depends on how far the cancer has spread.
As cancer treatments are often complex, hospitals use multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) to treat cervical cancer and tailor the treatment programme to the individual.
MDTs are made up of a number of different specialists who work together to make decisions about the best way to proceed with your treatment.
Your cancer team will recommend what they think the best treatment options are, but the final decision will be yours. In most cases, the recommendations will be:
- for early cervical cancer – surgery to remove the cervix and some or all of the womb, or radiotherapy, or a combination of both
- for advanced cervical cancer – radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy, and surgery is also sometimes used
Cervical cancer is often curable if it’s diagnosed at an early stage. When cervical cancer is not curable, it’s often possible to slow its progression, prolong lifespan and relieve any associated symptoms, such as pain and vaginal bleeding. This is known as palliative care.
Considering Complementary and Alternative Methods
You may hear about alternative or complementary methods that your doctor hasn’t mentioned to treat your cancer or relieve symptoms. These methods can include vitamins, herbs, and special diets, or other methods such as acupuncture or massage, to name a few.
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
3. HEART DISEASE
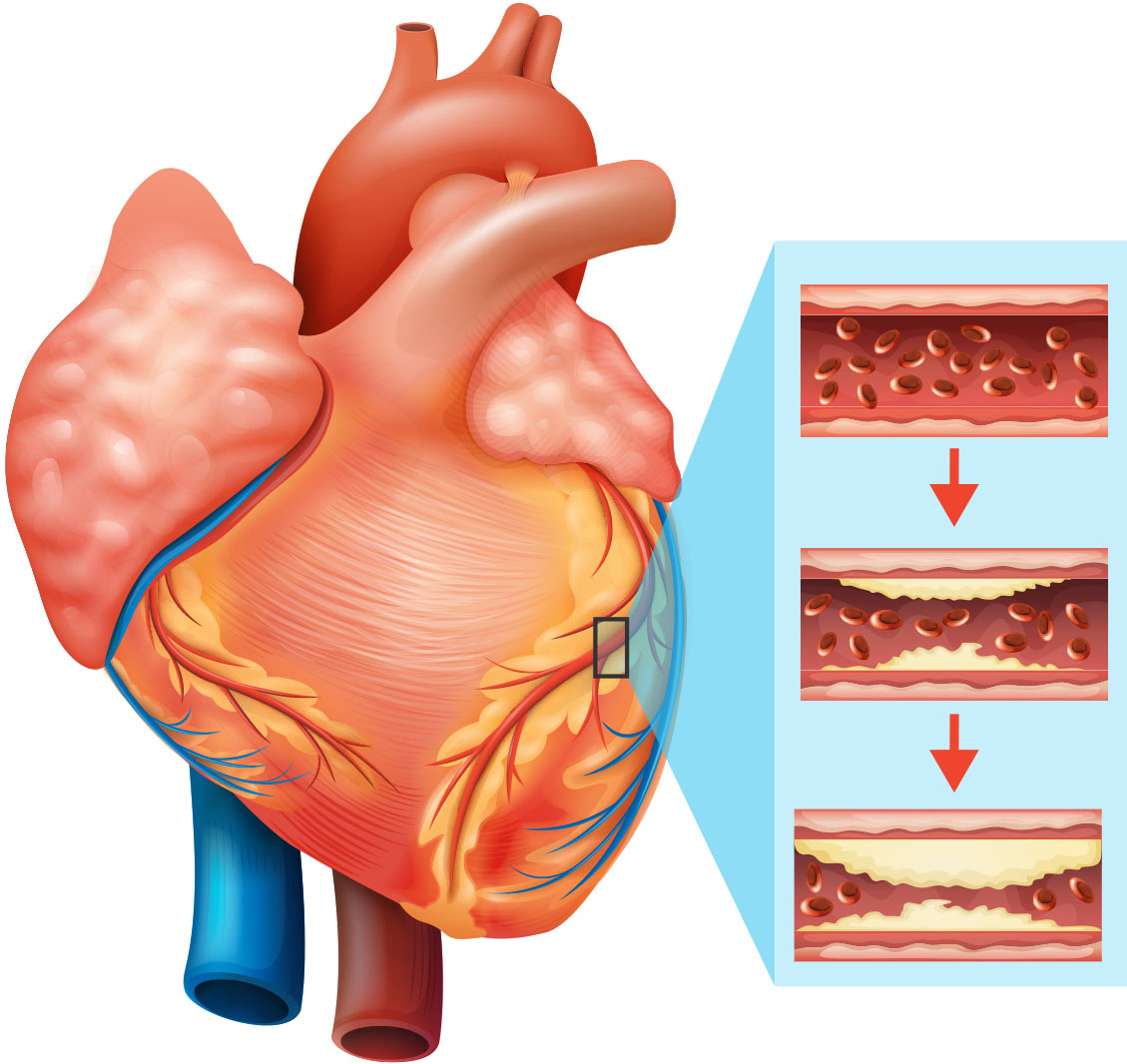
Although the public considers heart disease a common issue among men, the condition affects males and females nearly equally. Yet, only 54 percent of women realize that heart disease is the top health condition threatening their gender.
Some women suffer from pregnancy induced high blood pressure which can lead to complications or even death if not properly managed during delivery.
The term “heart disease” is often used interchangeably with the term “cardiovascular disease.”
Cardiovascular disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those that affect your heart’s muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease.
Heart disease is a name for several abnormal conditions of the heart and blood vessels. These include;
- coronary artery disease (blockages in the blood vessels around the heart)
- peripheral artery disease (blockages in the blood vessels in the arms or legs)
- problems with your heart’s rhythm (arrhythmia)
- problems with your heart’s muscles or valves (valvular heart disease)
- congestive heart failure (problem with the pumping or relaxation functions of the heart muscle
EARLY SIGNS OF HEART DISEASE
Many women don’t have any symptoms of heart disease until they have an emergency such as a heart attack. However, if you do have early symptoms, they may include;
- chest pain or discomfort, which can be either sharp, or dull and heavy (called angina)
- pain in your neck, jaw, or throat
- pain in your upper abdomen
- upper back pain
- nausea
- fatigue
- shortness of breath
- general weakness
- changes in skin color, such as grayish skin
- sweating
These symptoms may occur either while you’re at rest or during activities of daily life. These can also be the symptoms of a heart attack.
PREVENTING HEART DISEASE

The risk factors for heart disease are complicated and include genetics, other biological factors, and general health and lifestyle factors.
While you may not be able to completely eliminate your risk for heart disease, you can take steps to reduce it. These include;
- Get your blood pressure checked regularly. If it’s high, work with your doctor to lower it. This may include medication and lifestyle changes.
- If you smoke, seek help to quit. This can be difficult, but a doctor can help create a smoking cessation plan that’s right for you.
- If you have risk factors for diabetes, such as family history, get your blood sugar tested regularly.
- If you do have diabetes, keep blood sugar under control.
- Maintain a weight that works for your body.
- Eat a healthy diet that’s high in whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and lean meats.
- Limit your alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day.
- Manage stress levels.
- Get your cholesterol checked and take steps to lower high cholesterol if you need to.
- If you have sleep apnea, or believe you do, seek treatment.
- Exercise regularly.
- If you’ve had a heart attack, talk to your doctor about daily low-dose aspirin. This isn’t recommended for women who haven’t had a heart attack or stroke, as it can increase bleeding.
MANAGING A HEART DISEASE
When you have heart disease, there are little things you can do each day to make a big difference to your health.
- Food and fitness matter.
- It’s also important to reduce your stress and if you smoke, quit. And of course, take your medicines and keep up with your doctor appointments and cardiac rehab.
- Also, stay in touch with your mood. For many folks, depression comes along with heart disease. If you notice that’s true for you, talk to your doctor to get treatment.
4. GYNAECOLOGICAL HEALTH DISORDERS

Gynaecology is the medical practice dealing with the health of the female reproductive system (vagina, uterus, and ovaries).
Outside medicine, the term means “the science of women”. Its counterpart is andrology, which deals with medical issues specific to the male reproductive system.
A gynaacological disorder is a condition which affects the female reproductive organs, namely breast and organs in the abdominal and pelvic area including the womb (uterus), ovaries, Fallopian tube, vagina and vulva.
Virtually every woman will suffer a gynaecological condition at some point in her life. For most, it will be minor and easily treatable, but for others their condition may have devastating consequences- impacting their ability to have children and even, with some illnesses, threaten their life.
The most common top ten gynaecological disorders will be dealt with briefly in this article.
- Dysmenorrhea or painful menstruation
- Leucorrhea (excess white vaginal discharge)
- Amenorrhea or absence of period
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Vaginitis
- Menopause
- Pain during sex
SOME SYMPTOMS THAT YOU MIGHT HAVE GYNAECOLOGICAL DISORDER
- If you are getting your periods too early or too late.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding during periods or in between periods
- Pain in the pelvic area and it must not be related to menstrual cramps.
- Breast pain and Breast Lumps in Women.
- Burning sensation during passing urine.
- Vaginal bleeding while having sex or after having sex.
- Painful sexual intercourse.
- Itching, swelling or redness in vaginal area.
- Any abnormal lump or mass in the genital area.
- Increased vaginal discharge.
- Vaginal discharge with unpleasant odour or of unusual colour like green, yellow, or brown.
- Bleeding and discharge are a normal part of the menstrual cycle.
TREATMENT OF GYNAECOLOGICAL DISORDERS
There are several approaches to treating different gynaacological disorders so you might need to visit your healthcare giver. There are also herbal treatments that can be used to treat some of these conditions successfully.
5. PREGNANCY

Pregnancy, also known as gestation, is the time during which one or more offspring develops inside a woman. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy can occur by sexual intercourse or assisted reproductive technology.
A pregnancy may end in a live birth, abortion, or miscarriage, though access to safe abortion care varies globally. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period. This is just over nine months, where each month averages 31 days. When measured from fertilization it is about 38 weeks.
An embryo is the developing offspring during the first eight weeks following fertilization, after which, the term foetus is used until birth. Symptoms of early pregnancy may include missed periods, tender breasts, nausea and vomiting, hunger, and frequent urination. Pregnancy may be confirmed with a pregnancy test.
SYMPTOMS
- Missed periods
- Tender breasts
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hunger
- Frequent urination
COMPLICATIONS
- Miscarriage, high blood pressure in pregnancy, gestational diabetes, iron-deficiency anaemia, severe nausea and vomiting.
- Pre-existing conditions can worsen during pregnancy, threatening the health of a mother and her child. Asthma, diabetes, and depression can harm the mother and child during pregnancy if not managed properly.
- Pregnancy can cause a healthy mother’s red blood cell count to drop, a condition called anaemia, or induce depression. Another problem arises when reproductive cell implants outside the uterus, making further gestation unfeasible.
6. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
An autoimmune disease is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body. The immune system normally guards against germs like bacteria and viruses. When it senses these foreign invaders, it sends out an army of fighter cells to attack them.
Normally, the immune system can tell the difference between foreign cells and your own cells.
In an autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakes part of your body, like your joints or skin, as foreign. It releases proteins called autoantibodies that attack healthy cells.
Some autoimmune diseases target only one organ. Type 1 diabetes damages the pancreas. Other diseases, like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), affect the whole body.
CAUSES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes the immune-system misfire. Yet, some people are more likely to get an autoimmune disease than others.
According to a 2014 study, women get autoimmune diseases at a rate of about 2 to 1 compared to men — 6.4 percent of women vs. 2.7 percent of men. Often, the disease starts during a woman’s childbearing years (ages 15 to 44).
Autoimmune disease occurs when body cells that eliminate threats, such as viruses, attack healthy cells. As this condition continues to escalate among the population, researchers remain baffled as to why the condition affects mostly women.
Researchers suspect environmental factors like infections and exposure to chemicals or solvents might also be involved. A “Western diet” is another suspected risk factor for developing an autoimmune disease. Eating high-fat, high-sugar, and highly processed foods is thought to be linked to inflammation, which might set off an immune response. However, this hasn’t been proven.
SYMPTOMS OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
The early symptoms of many autoimmune diseases are very similar, such as:
- Fatigue
- Achy muscles
- Swelling and redness
- Low-grade fever
- Trouble concentrating
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Hair loss
- Skin rashes
TREATMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
Treatments can’t cure autoimmune diseases, but they can control the overactive immune response and bring down inflammation or at least reduce pain and inflammation.
7. FIBROIDS
![uterine_fibroids [TUSOM | Pharmwiki]](https://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/lib/exe/fetch.php/fibroids.png)
Fibroid, also called uterine myoma, is a noncancerous growth in the uterus that can develop during a woman’s childbearing years.
The causes of fibroids isn’t well understood. More than 100 thousand women battle with fibroids yearly (Nigeria). This may lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods and other conditions.
About 20% to 80% of women develop fibroids by the age of 50. In 2013, it was estimated that 171 million women were affected worldwide. They are typically found during the middle and later reproductive years.
After menopause, they usually decrease in size. In Nigeria, uterine fibroids are a common reason for surgical removal of the uterus.
SYMPTOMS
- Painful or heavy periods
- Pain during sex
COMPLICATIONS
USUAL ONSET
Middle and later reproductive years
CAUSES
Unknown
RISK FACTORS
- Family history
- Obesity
- Diet
- Genetics
- Early onset of puberty
DIAGNOSTIC METHOD
- Pelvic examination
- Medical imaging (ultrasound scan, etc)
TREATMENT
- Surgery
- Uterine artery embolization
- Herbal treatment
As women, it is important for us to understand that we are prone to any of these conditions, so we need to get familiar with these conditions so as to know what to do when we are faced with any of the symptoms, and also to get familiar with the preventive measures of these conditions.
If you currently suffer from any of the aforementioned health challenges and disorders and you desire a holistic natural remedy, do not hesitate to contact us.
Stay healthy and never give up!
Plan B Wellness Limited
IG/Twitter: planbwellness
Tel/Whatsapp: +2348099666650












